The precisionbind Human Interleukin 4 (IL-4 / IL4) ELISA includes features like:
– Ready to use protocol with break-apart wells for ease of use
– Standardisation and High Reproducibility
– Lot to Lot Consistency
– Accuracy and Precision
Principle Of Assay: This ELISA is a sandwich immunoassay. Antibodies are coated on 96 well plates. The antigen protein present in sample and standard respectively bind to the coated wells. The wells are washed and an antibody:HRP Conjugate is added which binds to the bound complex in the well. Washing is performed to remove any unbound material. TMB substrate is added and the enzyme reaction is stopped by dispensing of stop solution into the wells. The optical density (OD) of the solution at 450 nm is directly proportional to the amount of antigen protein present in the standard or samples.
Disclaimer: The data indicated herein with specifications are changed from time to time at time of production of the assay. We request you to confirm the specifications including the assay range and procedure as per the most current IFU (instructions for use) accompanying the assay kit.
Validated against seven points for a “GOLD RING” Standard Quality ELISA – the benchmark sign for Krishgen Quality. The The precisionbind ELISA kits are used for assessing the specific biomarker in samples analytes which may be human serum, plasma, biological fluids and cell culture supernatant. The kit uses indirect sandwich assay with double antibodies – capture and detection to ensure a high degree of sensitivity and specificity in the estimation of Interleukin 4 (IL-4 / IL4);
About PrecisionBind:
PrecisionBind is Krishgen`s cytokine ELISA platform developed for bioanalytical robustness in translational research, including immuno-oncology and cell & gene therapy programs. Where applicable, kit standards are calibrated against NIBSC/WHO international standards to support unit traceability and inter-study comparability.
Assays are characterized following ligand-binding assay performance expectations, including:
All kits are Research Use Only (RUO) and not intended for diagnostic use.
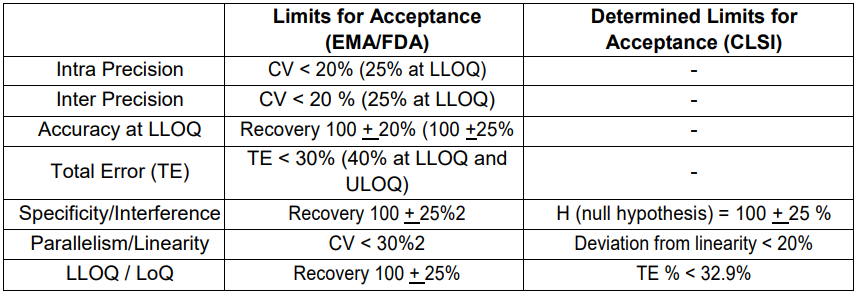
Validation Parameters and Acceptance Criteria
1. IL 4 Cmax Values and Recommended ELISA Range
Note: Assay sensitivity < 1-2 pg/mL recommended for baseline detection; upper limit ? 10,000 pg/ml advised for CRS monitoring.
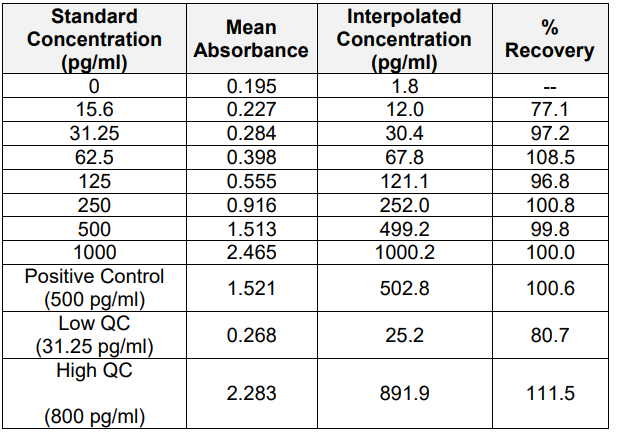
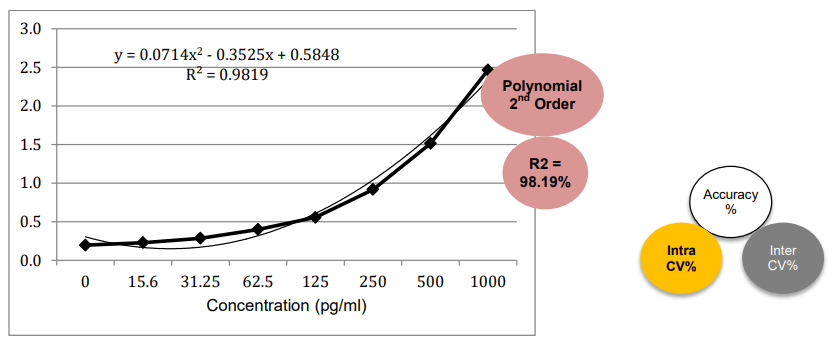
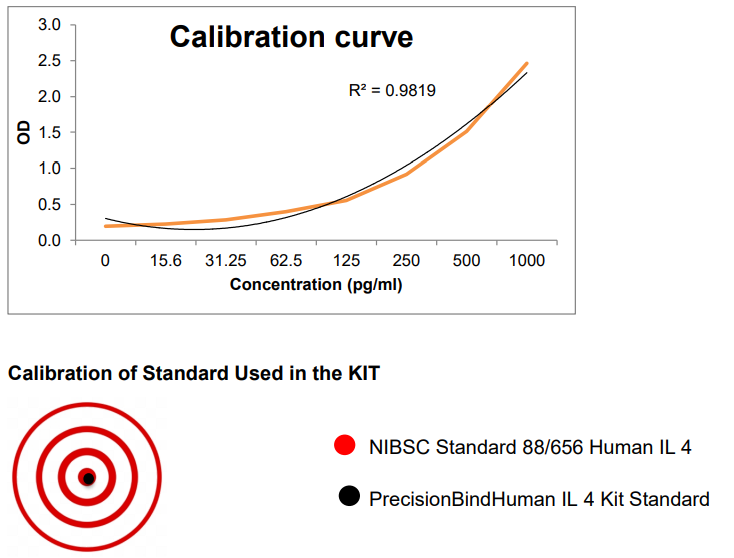
The PrecisionBind Human IL 4 ELISA kit is developed using an assay range of 15.6 – 1000 pg/ml with the dilutional linearity accuracy to measure responses as per the application table above on patient Cmax values. The kit has also been validated upto 16 fold dilution
and the values are within the acceptable range
2. Specificity and Selectivity
2.1 Specificity The capture antibody and detection antibody are both specific to IL 4 and are monoclonal antibodies. They show a high affinity to bind to native as well as recombinant IL 4.
2.2 Selectivity
The ELISA has no or low cross reactivity to IL?1? (IL-1beta), IL?6, or TNF?? (TNFbeta).
2.3 NIBSC validation
The standard used in the kit is calibrated against an international standard from the National Institute of Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC), Potters Bar, Hertfordshire EN6 3QG, UK. 1 ng of supplied standard equals 14 U of 88/656 NIBSC-standard.
Therefore 1000 pg/ml is equivalent to 14 U of IL-4 as per NIBSC.
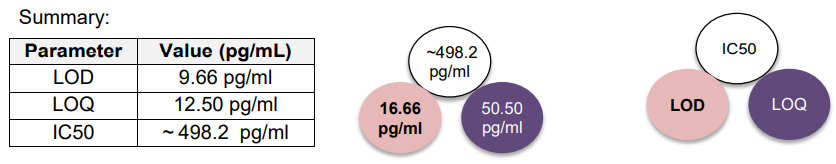
2.4 LOD, LOQ and IC50
LOD (Limit of Detection)
The lowest analyte concentration that can be reliably distinguished from blank/background noise but not necessarily quantified precisely.
Statistically:
LOD = Mean of Blank + 3X SD of Blank
(3? criterion is most common).
LOD for PrecisionBind Human IL 4 ELISA = 9.66 pg/ml
LOQ (Limit of Quantitation)
The lowest analyte concentration that can be quantified with acceptable accuracy and precision.
Statistically:
LOQ = Mean of Blank + 10X SD of Blank (10? criterion is most common).
LOQ for PrecisionBind Human IL 4 ELISA – 12.50 pg/ml
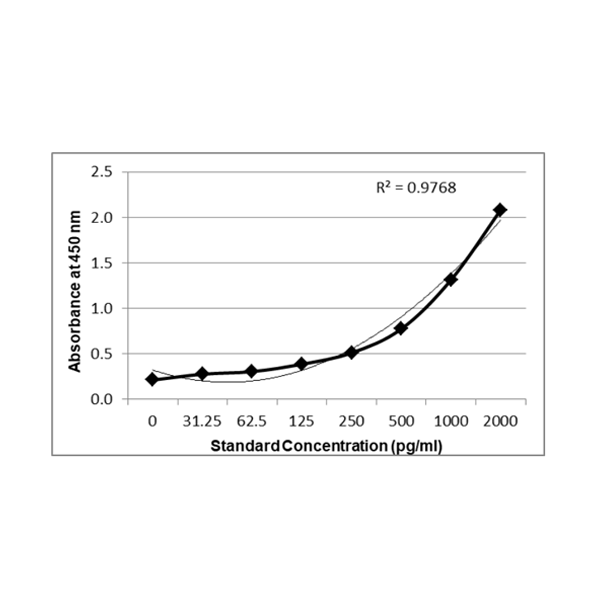
IC50 in ELISA (Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration)
IC50 = The concentration of an inhibitor (drug, antibody, compound) required to reduce the signal (e.g., binding, enzymatic activity) by 50% compared to the maximum signal in the assay.
In ELISA, this is commonly used for: Neutralization ELISA: Quantifies potency of antibodies inhibiting target?ligand interaction.
Drug Potency Testing: Measures concentration at which drug inhibits 50% of target activity.
IC50 for PrecisionBind Human IL 4 ELISA = ~ 498.2 pg/ml
Regulatory Note:
LOD *S/N ? 3:1, LOQ ? 10:1, %CV ? 20% *S/N = Signal / Noise Ratio
3. Linearity and Range
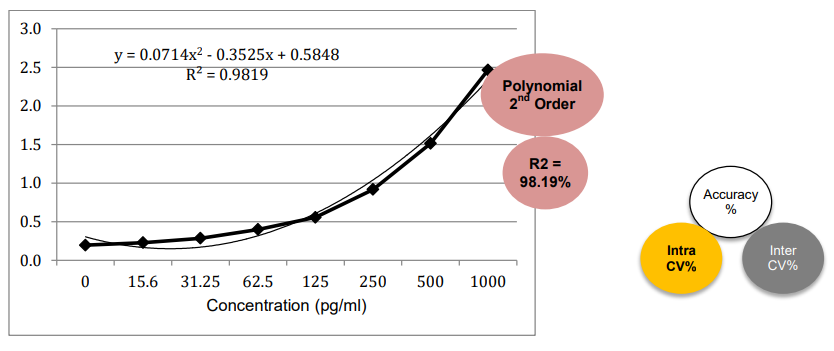
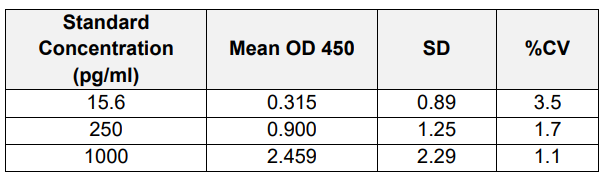
4. Accuracy and Precision (Intra / Inter-Assay)
A) Intra-Assay:
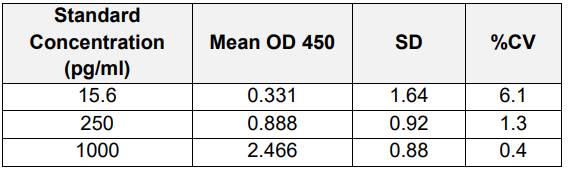
B) Inter Assay:
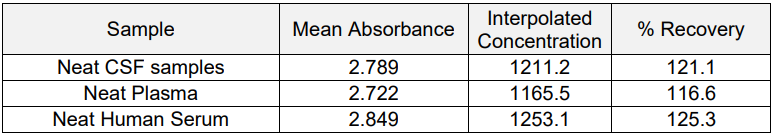
5. Parallelism and Matrix Effect
Sample Dilution factor ? Human Serum, Human Plasma and Human CSF samples have been tested. Neat samples can be run directly.
Neat Human Serum, Human Plasma and Human CSF were spiked with 1000 pg/ml Human IL-4 and ELISA assay was run.
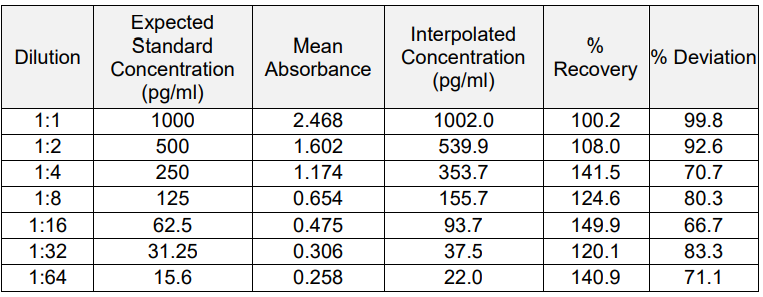
A) Serum:
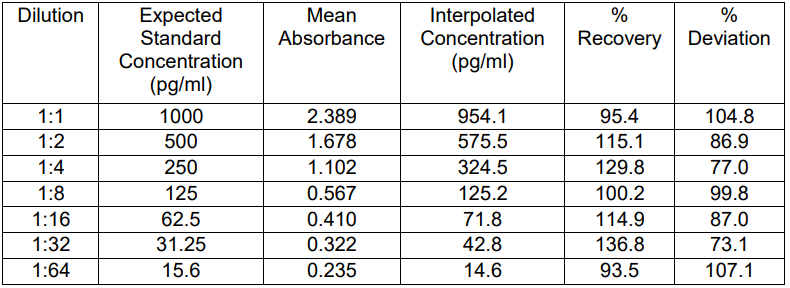
B) Plasma:
C) Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF):

Results:
i) Parallelism is maintained across the 1:1 to 1:16 dilutions.
ii) % Recovery for most dilutions falls within the acceptable range of 80%?120%.
iii) No significant matrix effect observed at higher dilutions.
iv) The PrecisionBind Human IL-4ELISA kit was tested for matrix effect on human serum, plasma, CSF and physiological buffer 7.4 to mimic tear fluid samples.
6. Sample Handling and Storage Conditions
A.) Sample collection and handling: Specimens should be clear and non-hemolyzed. Samples should be run at a number of dilutions to ensure accurate quantitation.
Cell Culture Supernatant: If necessary, centrifuge to remove debris prior to analysis. Samples can be stored at temperature <-20?C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Serum: Use a serum separator tube and allow clotting for 30 minutes, then centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1000 x g. Remove serum layer and assay immediately or store serum samples at temperature <-20?C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Plasma: Collect blood sample in a citrate, heparin or EDTA containing tube. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1000 x g within 30 minutes of collection. Assay immediately or store plasma samples at temperature <-20?C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
B.) Storage conditions:
Store main kit components at 2-8?C.
Store recombinant lyophilized standard at 2-8?C. Upon reconstitution aliquot standards into polypropylene vials and store at -20?C as per assay requirements. Do not freeze thaw for more than two times.
Before using, bring all components to room temperature (18-25?C). Upon assay completion return all components to appropriate storage conditions.
Matrix Effect Heat Map

Determined Limits for Acceptance according to EMA/FDA and CLSI regulations
References
Keegan, A. D., Leonard, W. J., & Zhu, J. (2021). Recent advances in understanding the role of IL-4 signaling. Faculty Reviews, 10. https://doi.org/10.12703/r/10-71
Brown, M. A., & Hural, J. (2017). Functions of IL-4 and control of its expression. Critical Reviews in Immunology, 37(2?6), 181?212. https://doi.org/10.1615/critrevimmunol.v37.i2-6.30
FDA Guidance for Industry: Immunogenicity Assessment for Therapeutic Protein Products (2014).
EMA Guideline on Biosimilar Monoclonal Antibodies (2012)