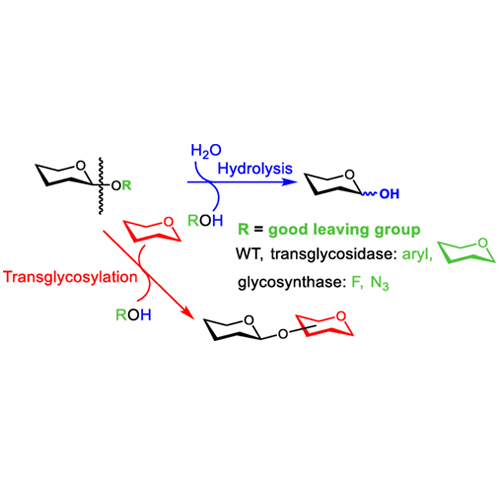
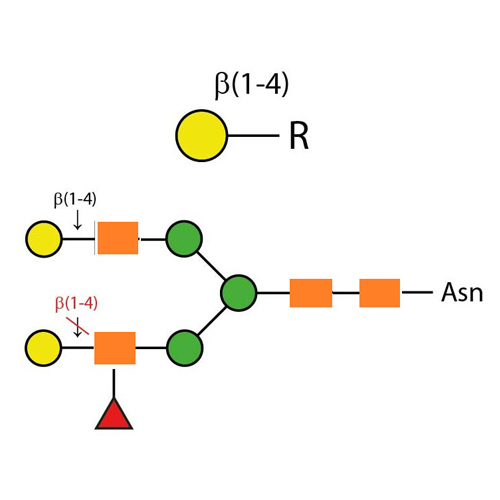
Krishzyme beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, N-acetyl-beta-d-glycosaminide N-acetylglucosaminohydrolase, glucosaminidase, hexosaminidase cleaves all non-reducing terminal -linked N-acetylglucosamine residues from complex carbohydrates and glycoproteins. The cleavage rates of different linkages of GlcNAc on bi-, tri- and tetraantennary oligosaccharides is greatly dependent on the steric hindrance by neighbouring residues. The beta(1-2)GlcNAc residue linked to the beta(1-3)-linked mannose is cleaved at the highest rate and the beta(1-2) GlcNAc residue linked to the beta(1-6)-linked mannose at the lowest rate for all three oligosaccharides. The beta(1-6) GlcNAc residue, when present, is removed at the second highest rate and the beta(1-4) GlcNAc, third. On a triantennary structure, this residue is removed at the second highest rate. A bisecting beta(1-4) GlcNAc linked to the beta-linked mannose severely hinders cleavage of other GlcNAc residues high concentrations of enzymes and prolonged incubation times are required for cleavage. 1 unit of Krishzyme N-acetylglucosaminidase is defined as the amount of enzyme required to produce 1 umole of p-nitrophenol in 1 minute at 37 C, pH 5.0 from p-nitrophenyl-Beta-D-N-acetyl-glucosaminide
Additional information
| Pack Size | 4 U / 50 ul |
|---|---|
| Shipping Temperature | 2-8 Deg C, gel pack |
| Storage Temperature | Refrigerate at 2-8C |
| Regulatory Status | For Research Use Only |