Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, characterized by the progressive degeneration of neurons in the brain, pose significant challenges to global health, affecting millions of individuals worldwide.
Several specific therapeutic strategies are being explored and investigated for treatment. Neurological disease markers generally have proven elusive for conclusive results, but remain an interesting and promising field of research.
Whether it’s Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s, or more complex spectrum disorders like autism or other auto-immune neural diseases like MS, understanding neuroinflammation and neurological biomarkers might allow for earlier detection and controlling symptoms.
Krishgen has a range of ELISA including biomarkers and specific mAb drug PK and ADA ELISA for neuro-degenerative research.
mAb Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases
Monoclonal antibodies are engineered immune system proteins that bind specifically to disease-associated targets, such as misfolded proteins or toxic aggregates, facilitating their clearance or neutralization. Here are some key findings and trends in the development of mAb drugs for neurodegenerative diseases:
Amyloid-beta-targeted mAbs for Alzheimer’s disease: Amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. Recent clinical trials have explored mAbs that target Aβ, aiming to reduce plaque accumulation and subsequent neurodegeneration. Promising results have been demonstrated by mAbs such as aducanumab, gantenerumab, solanezumab and crenezumab which showed a reduction in cognitive decline in clinical trials.
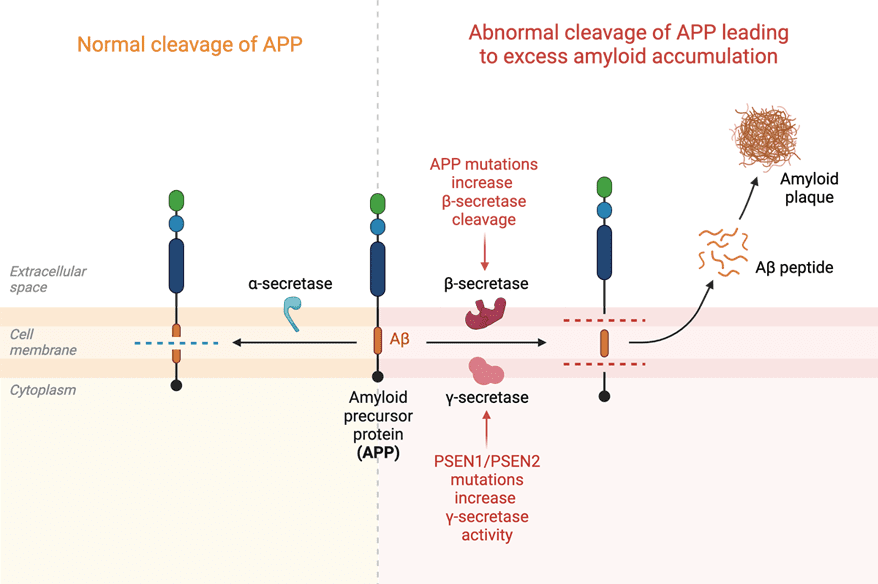 Created by biorender.com
Created by biorender.com
Tau-targeted mAbs for Alzheimer’s and other tauopathies: The accumulation of abnormal tau protein is another characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease. Emerging research is focused on developing mAbs that selectively bind to abnormal tau, potentially preventing its aggregation or promoting its clearance, like Lecanemab. These therapies hold promise for tackling both Aβ and tau pathology simultaneously.
Alpha-synuclein-targeted mAbs for Parkinson’s disease: The aggregation of alpha-synuclein protein is a hallmark feature of Parkinson’s disease. Novel mAbs are being developed to bind to alpha-synuclein and prevent its aggregation, thereby slowing down or halting disease progression. Several experimental mAbs have demonstrated efficacy in preclinical models and are advancing towards clinical trials.

alpha-Synuclein aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease. Created by biorender.com
Alternative Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases
In addition to mAb drugs, other innovative therapeutic approaches are also being explored to combat neurodegenerative diseases. Some noteworthy developments include:
BiTE (Bispecific T-cell Engager) antibodies: Novel antibodies that can simultaneously bind to both disease-causing proteins and immune cells, facilitating clearance of toxic protein aggregates. BiTE antibodies targeted to alpha-synuclein are currently in preclinical development for Parkinson’s disease.
Gene therapies: Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, show promise in correcting disease-causing genetic mutations associated with neurodegenerative diseases. By precisely modifying the genes responsible, gene therapies hold potential for halting or even reversing disease progression.
Small molecule inhibitors: In addition to mAbs, small molecule inhibitors are being investigated to target specific disease-related pathways and proteins implicated in neurodegeneration. For example, small molecules that inhibit the enzyme responsible for producing Aβ have shown encouraging results in preclinical studies. Beta-secretase (BACE) inhibitors, specifically, that target the enzyme responsible for producing Aβ precursor protein (APP), with several inhibitors are currently in development for Alzheimer’s disease.
Neuroprotective peptides: Peptides derived from natural sources or designed de novo have demonstrated neuroprotective properties in preclinical studies. These peptides can inhibit toxic protein aggregation, promote neuronal survival, and enhance brain repair processes, offering potential therapeutic avenues for neurodegenerative diseases.
CRISPR-Cas9: A genome editing technology being investigated for the correction of genetic mutations associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Huntington’s disease and ALS.
PGC-1alpha gene: A target gene for gene therapy aimed at mitochondrial protection and neuronal function preservation in Parkinson’s disease.
Future Trends and the Path Forward
As research in mAb drugs and other therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases continues to expand, several key trends and future directions are emerging:
Combination therapies: Multiple therapeutic modalities, such as mAbs with small molecules or gene therapies, are likely to be combined to improve treatment efficacy. The synergy achieved through combination therapy may enhance disease-modifying effects and increase the chance of successful outcomes.
Early intervention: There is growing evidence to suggest that early intervention before significant neuronal loss occurs may yield more favourable treatment outcomes. The identification of reliable biomarkers and the development of diagnostic techniques for early disease detection will be crucial to implement timely intervention strategies.
Patient-centric approaches: Future research will focus on tailoring therapies to individual patients based on their genetic profile and disease progression. This personalized medicine approach will enable more accurate diagnosis and treatment selection, optimizing therapeutic outcomes for neurodegenerative diseases.
References:
Sharma, M., and Gupta, P. K. (2020). Gene editing tools for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, 1039, 1-24.
Yan, R. (2017). Small molecule inhibitors as therapeutic agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 9, 1-15.
Seilheimer, B., et al. (2019). Natural peptides with neuroprotective actions against Aβ aggregation. Journal of Peptide Science, 25(10), e3194.
Bally, B., et al. (2019). Combination therapy for neurodegenerative diseases: Is there a rational clinical perspective? Pharmacological Research, 141, 303-327.
