The development of alternative, patient-friendly drug delivery routes for peptide-based therapeutics continues to be a major focus in pharmaceutical research. At the Drug Delivery to the Lungs (DDL) Conference 2025, a peer-reviewed study presented by Glieca et al. explored an innovative approach to delivering semaglutide, a widely used GLP-1 receptor agonist, via the pulmonary route.
A critical component of this research was the ability to accurately quantify semaglutide in biological samples to generate reliable pharmacokinetic (PK) data. This was achieved using the KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide (Ozempic™) ELISA developed by Krishgen Biosystems, underscoring the importance of validated ELISA assays in translational drug delivery research.
Background: Why Pulmonary Delivery of Semaglutide?
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists play a pivotal role in the management of type 2 diabetes and obesity by regulating glucose metabolism and appetite. Semaglutide, in particular, has gained widespread clinical adoption due to its prolonged half-life and proven efficacy. However, its current administration routes-primarily subcutaneous injection and oral delivery-present challenges related to patient compliance and gastrointestinal degradation.
Pulmonary delivery offers an attractive alternative. The lungs provide a large surface area, extensive vascularization, and the potential for rapid systemic absorption, bypassing enzymatic degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Despite these advantages, delivering peptide drugs to the lungs requires careful formulation design and, critically, robust bioanalytical methods to evaluate systemic exposure.
Study Objectives and Design
The paper presented at DDL 2025 study aimed to evaluate whether an engineered dry powder formulation of semaglutide could be effectively delivered via inhalation and achieve meaningful systemic exposure in vivo. The key objectives included:
- Developing a spray-dried semaglutide powder optimized for pulmonary delivery
- Assessing in vitro safety using A549 lung epithelial cells
- Comparing the pharmacokinetic profile of intratracheal (IT) administration with conventional subcutaneous (SC) dosing in rats
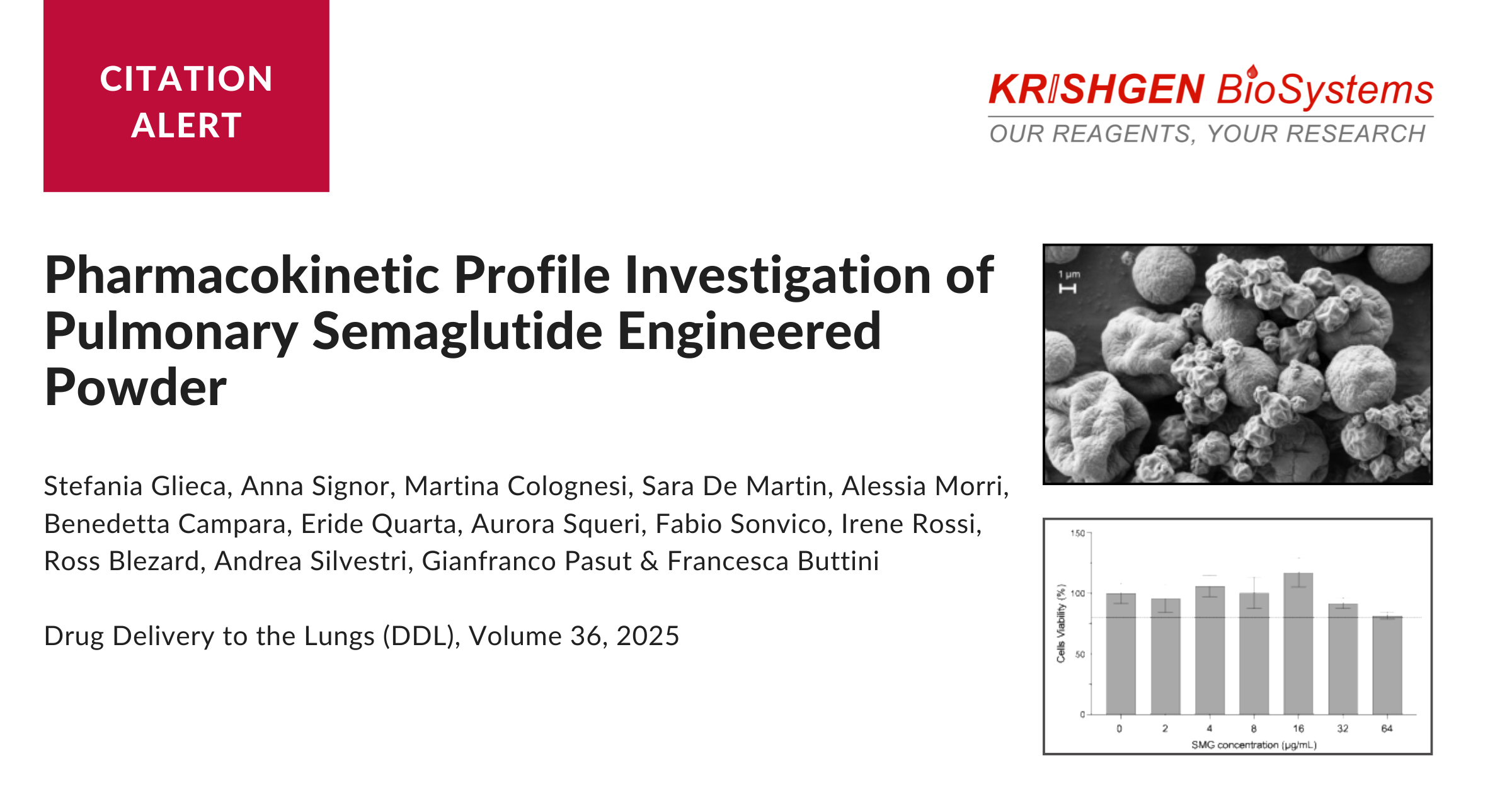
To achieve these goals, semaglutide was spray-dried using trehalose as the primary excipient, with L-leucine added to enhance powder dispersibility. The resulting formulation demonstrated strong aerodynamic performance, making it suitable for deep lung deposition.
Key Findings from the Paper
1. Efficient Powder Engineering and Aerosol Performance
The spray-drying process yielded a highly respirable powder with a production yield exceeding 75%. Aerodynamic characterization using a Next Generation Impactor (NGI) showed a fine particle fraction (FPF) of approximately 43%, indicating effective delivery to the lower respiratory tract. Particles were predominantly in the 3-4 µm range, ideal for alveolar deposition.
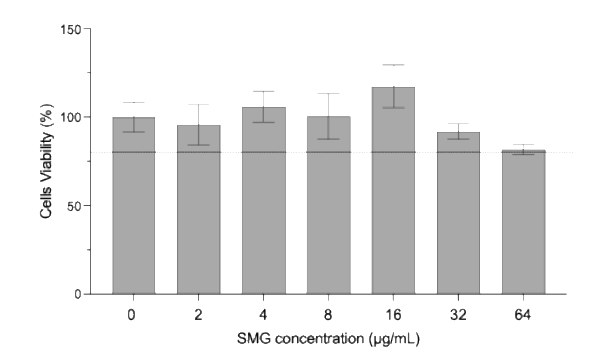
Figure: A549 cells viability (%) after treatment with resuspended spray-dried powder to obtain different SMG concentrations (n=3, mean ± std deviation).
2. Favourable In Vitro Safety Profile
Cytotoxicity was evaluated using an MTT assay on A549 cells, a standard in vitro model for pulmonary safety assessment. Semaglutide demonstrated no significant cytotoxicity at concentrations up to 64 µg/mL, supporting the suitability of the formulation for pulmonary administration.
3. Rapid Systemic Absorption Following Pulmonary Delivery
In vivo pharmacokinetic studies in Sprague-Dawley rats revealed that intratracheal administration of semaglutide resulted in rapid systemic absorption, with a Cmax of 0.341 µg/mL achieved at 3 hours. In comparison, subcutaneous administration reached a slightly higher Cmax (0.406 µg/mL) at a later time point (4 hours).
While the overall exposure (AUC) following IT administration was lower than SC dosing – as expected due to partial dose loss and route-dependent bioavailability the data clearly demonstrated that semaglutide was promptly absorbed through the lungs. Importantly, the PK profiles were consistent with previously reported literature, reinforcing the translational relevance of the findings.
The Role of KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide ELISA in PK Analysis
Krishgen was pleased to note that the quantitative measurement of serum semaglutide concentrations, which directly informed all PK parameters, including Cmax, Tmax, and AUC was performed using Krishgen’s Semaglutide ELISA kit. According to the Methods section of the study presented at the Drug Delivery to the Lungs (DDL) Conference 2025, serum samples collected from both intratracheal and subcutaneous dosing groups were analyzed using the KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide (Ozempic™) ELISA by Krishgen Biosystems, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
This highlights a crucial point: the reliability of PK conclusions is only as strong as the analytical method used to generate the data.
Why Accurate ELISA Measurement Is Critical in PK Research
Pharmacokinetic studies, particularly for peptide-based therapeutics, demand analytical tools that combine high sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility. In pulmonary delivery research, this need becomes even more pronounced due to:
- Lower systemic concentrations compared to injectable routes
- Complex biological matrices such as serum and plasma
- The requirement to detect subtle differences between delivery routes
ELISA remains a preferred technique for peptide quantification because it enables selective detection of intact analyte, minimizes interference, and supports high-throughput analysis. In the DDL 2025 study, the use of a validated ELISA ensured confidence in the measured concentration time profiles, enabling meaningful comparisons between pulmonary and subcutaneous administration.
The successful application of KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide ELISA in this peer-reviewed research demonstrates its suitability for preclinical PK studies, inhalation models, and translational drug delivery programs.
Access the Full Study and Learn MoreThe complete research paper, “Pharmacokinetic Profile Investigation of Pulmonary Semaglutide Engineered Powder,” was presented at the Drug Delivery to the Lungs Conference 2025 and provides detailed insights into formulation development, in vitro characterization, and in vivo pharmacokinetics.
Download the DDL 2025 paper to explore the full methodology and results. Contact Krishgen Biosystems to learn how KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide ELISA can support your GLP-1, inhalation, or pharmacokinetic research programs.
Conclusion
The study demonstrates that pulmonary delivery of semaglutide is a scientifically sound and promising approach, supported by robust formulation science and validated pharmacokinetic analysis. Central to this work was the ability to accurately quantify semaglutide in serum using KRIBIOLISA™ Semaglutide ELISA by Krishgen Biosystems.
As pharmaceutical research continues to push the boundaries of drug delivery innovation, reliable ELISA-based bioanalysis will remain essential for generating data that is reproducible, interpretable, and translatable. Krishgen is proud to support such cutting-edge research by providing trusted immunoassay solutions to the global scientific community.