Immuno-Oncology
Non-surgical treatments of cancer (mainly conventional chemotherapy, targeted biological therapies, and radiotherapy) have not generated completely satisfactory results to date. The ongoing problems include low target selectivity, drug resistance, inability to effectively address metastatic disease and severe side effects. In contrast, immunotherapies that overall provoke host immunity to induce a systemic response against tumors currently offer much clinical promise. Immuno-oncology remains a growing subspeciality of cancer treatments, with several drugs already approved by the US FDA / EMA, and at least 150+ in clinical trials currently.
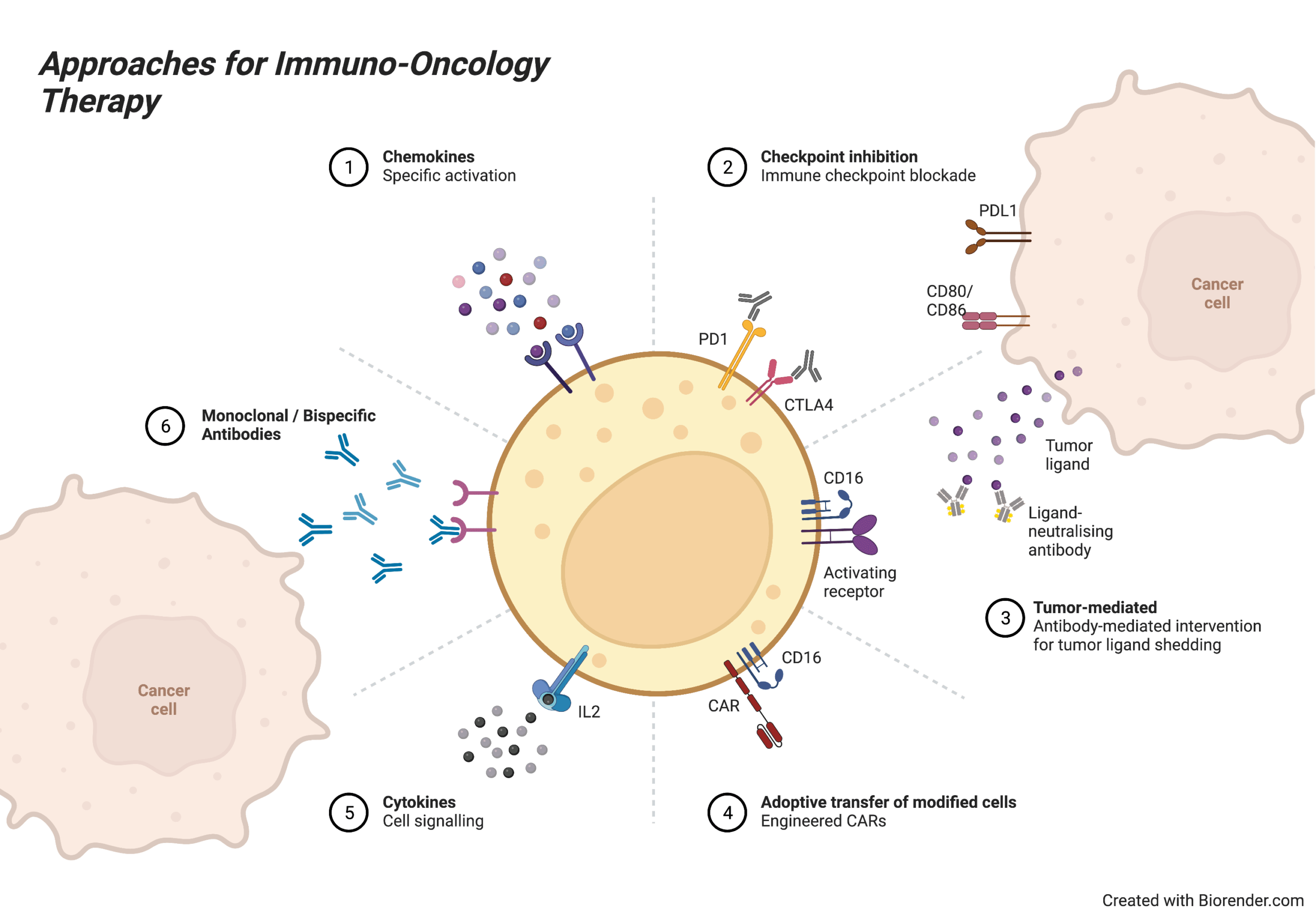
Antibody therapies aim to increase the activity of the immune system without specifically targeting cancer cells. For example, cytokines directly stimulate the immune system and increase immune activity. Checkpoint inhibitors target proteins (immune checkpoints) that normally dampen the immune response. This enhances the ability of the immune system to attack cancer cells. Current research is identifying new potential targets to enhance immune function. Approved checkpoint inhibitors include antibodies such as ipilimumab, nivolumab, and pembrolizumab.
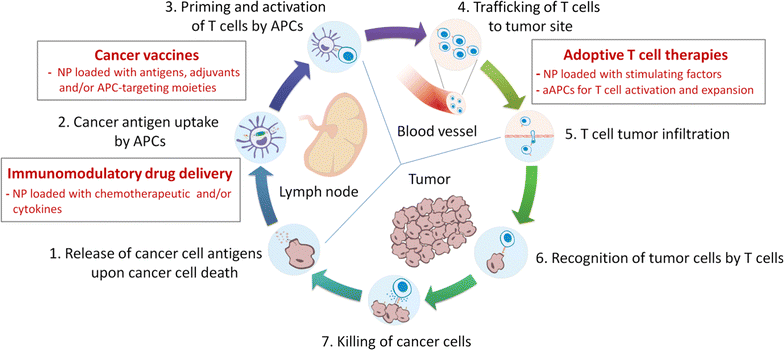
The cancer immunity cycle. Diagram illustrating the seven major steps involved in the generation of an immune response against cancer with main bioengineering approaches developed so far (in red). aAPCs artificial antigen presenting cells, APCs antigen presenting cells, NPs nanoparticles. Adapted from Chen DS, Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer‑immunity cycle. Immunity. 2013;39:1–10. Content available from Journal of Translational Medicine.
Recent breakthroughs in immuno-oncology research translate into a paradigm shift with regards to attacking advancing cancer. The benefits of immuno-oncology have resulted in long-lasting tumor regression where surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy proved less effective.
There are several approaches within immuno-oncology research, including checkpoint inhibitor therapy, adoptive cell therapy (ACT), dendritic cell therapy, and cancer vaccine development.
- PD-1, PDL-1 inhibitors work by interfering with PD-1 or PDL-1 proteins that prevent the body’s immune system from attacking cancer cells. Drugs in this category include nivolumab (Opdivo), atezolizumab (Tecentriq), pembrolizumab (Keytruda), avelumab (Bavencio), durvalumab (Imfinzi) and cemiplimab (Libtayo).
- CTLA-4 inhibitors seek out and lock onto cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), a protein that helps keep immune system cells deactivated. Ipilimumab (Yervoy) is designed to help the immune system destroy cancer cells by blocking the action of CTLA-4.
- LAG-3 inhibitors attach to and block a protein that keeps the immune system in check. Relatlimab, in combination with the PD-1 inhibitor nivolumab, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2022. The combination, known as Opdualag, can be used to treat melanoma and is being studied for use in other types of cancer.
Learn more about Krishgen’s range of ELISA for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor molecules and mAb drugs here.
In addition to checkpoint inhibitors, immunotherapy approaches fall into the following main categories:
- Monoclonal antibodies are lab-generated proteins that target specific tumor antigens (substances that the immune system sees as being foreign or dangerous). Some monoclonal antibodies help the immune system recognize and destroy cancer cells. Monoclonal antibodies used in the treatment of certain cancers include rituximab (Rituxan) and trastuzumab (Herceptin).
- Bispecific antibodies are lab-generated proteins that target specific tumor antigens (as do monoclonal antibodies) but also bind proteins on the surface of immune cells (T-cells). This allows the T-cells to get close to and destroy the cancer cells. Blinatumomab (Blincyto) is an example of a bispecific antibody.
- Therapeutic vaccines can boost the immune system and have the potential to treat cancer or prevent it from recurring (coming back) after treatment. The FDA has approved vaccines for certain cancers. Additionally, a number of vaccines are being studied in clinical trials.
- Adoptive T-cell transfer (also called cellular adoptive immunotherapy) is an approach in which T-cells are removed from the individual, grown to an increased number in a laboratory and infused back into the individual with the goal of improving the immune system’s anti-cancer response. One type of adoptive T-cell transfer is chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, which is used to treat certain blood cancers.
B7-CD28 Ligand-Receptor Family ELISA
Chemokines and Chemokine Ligands ELISA
Cytokines and Cytokine Receptors ELISA
MHC Class I ELISA kits
TIM Family ELISA
TNF and TNF-R Superfamily ELISA
VEGF and VEGF Receptor ELISA
Other Protein and Enzyme ELISA
